What is Arthritis? How to Relieve Arthritis Pains
The NJ Pain & Spine blog addresses a variety of pain disorders and provides resources for patients who suffer from muscle and joint discomfort. This edition aims to educate people on recognizing body pains such as arthritis early on and how to relieve these pains.
Arthritis is a common disease that occurs when there is swelling and tenderness in one or more joints. Joint stiffness and pain minimize physical mobility and create discomfort and chronic pain.
There are more than 100 types of arthritis and related conditions; the four most common types are:
Osteoarthritis: The most common type of arthritis. A disease of the whole joint, where bones in affected joints weaken, the connective tissue that holds the joint together deteriorates, and inflammation damages the joint lining.
Autoimmune Inflammatory Arthritis: Occurs when the immune system is overactive. In response, the immune system attacks healthy tissue, including joints in the spine, hands, and feet. The inflammation may evolve systemic, harming the eyes, skin, heart, and other organs.
Infectious Arthritis: When a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection triggers arthritis.
Gout (metabolic arthritis): Results from buildup in joints of painful uric acid crystals.
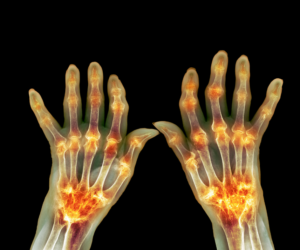 Major Demographic
Major Demographic
The risk of developing most types of arthritis increases with age. Most types of arthritis are more common in women; nearly 60% of all people with arthritis are women. Ankylosing spondylitis (an inflammatory disease) and gout are more common in men. More statistics are listed below.
- An estimated 21.2% (18.7% age-standardized) of U.S. adults 18 years old and younger (53.2 million) are diagnosed
- Higher demographic among women (20.9%) than men (16.3%)
- Veterans (24.2%) versus nonveterans (18.5%)
- Non-Hispanic White (20.1%)
- Hispanic or Latino (14.7%)
- Non-Hispanic Asian adults (10.3%)
- Adults younger than 45 years old represent 88.3% of all U.S. adults with arthritis
- Unadjusted arthritis prevalence is high among adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (57.6%)
How it is Diagnosed
A variety of methods diagnoses arthritis.
- Patient’s medical history
- Physical examination
- X-rays, laboratory tests, imaging tests (ultrasound or MRI)
- Blood tests
- Perform an arthrocentesis (procedure of removing fluid from a joint)
With autoimmune and inflammatory types of arthritis, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to preventing permanent joint damage.
Relief Techniques
While there is no current cure for arthritis, some methods provide temporary relief to make living with arthritis more bearable.
- Heat and cold
- Heating pads, hot baths or showers, or warm paraffin wax can help reduce joint pain. Please avoid leaving the heat on the joints for longer than twenty minutes.
- Ice packs can soothe aches and reduce inflammation, especially after exercise.
- Massage
- Massages reduce pain and stiffness. Make sure your massage therapist knows what areas of the body your arthritis is prone to.
- Physical activity
- Physical activity, as long as it is low-impact, lessens joint pain, builds muscle, and enhances the range of motion. Low-impact physical activity puts less stress on the body, which lowers the risk of injury. Daily stretches, walks, yoga, and swimming are optimal forms of exercise.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Weight Management
- Being overweight can increase complications of arthritis.
- Quit smoking.
- Smoking induces stress on connective tissues, which results in arthritis pain.
- Relaxation therapy
- Relaxation activities such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga ease arthritis pain.
- Joint Pain Medicine
- Over-the-counter medications reduce inflammation.
- Weight Management
How Does Arthritis Impact Daily Life?
Arthritis can lead to severe joint pain, which can be a negative influence on a person’s daily life. Severe arthritis affects mental health, a person’s capability to work in productive environments, and engagement in physical activities. Although arthritis is not a life-threatening disease, it can worsen the quality of life detrimentally. Arthritis can incur pain, disability, and premature death.
What Happens if Arthritis Isn’t Properly Treated? Why is it Important to Relieve Arthritis Pain
Untreated arthritis may progress and worsen over time. The disease cannot kill you, but the chronic pain that is associated with arthritis can be a huge hindrance to a comfortable life. At NJ Pain & Spine, we devote ourselves to providing exemplary quality back and pain management service. If you have arthritis or joint pain, schedule an appointment at NJ Pain & Spine to ensure relief today.




